Compare, Calculate, and Interpret Yield Spread Measures |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › corporate bond yield spread › Compare, Calculate, and Interpret Yield Spread Measures |
Compare, Calculate, and Interpret Yield Spread Measures
|
Yield spread (measured in basis points) is the difference between any two bond issues and is computed as follows:
Yield spread = Yield on Bond 1 – Yield on Bond 2
When the second bond is a benchmark (i.e. Treasury), the yield spread is referred to as the absolute yield spread. What Causes Spread?
Spread can be attributed to macroeconomic factors affecting the bond issuer as well as the bond itself. These include factors such as credit risk, liquidity, and taxation. The benchmark (risk-free rate) considers the expected rate of inflation, exchange rates, the impact of fiscal/monetary policies, and general economic growth. 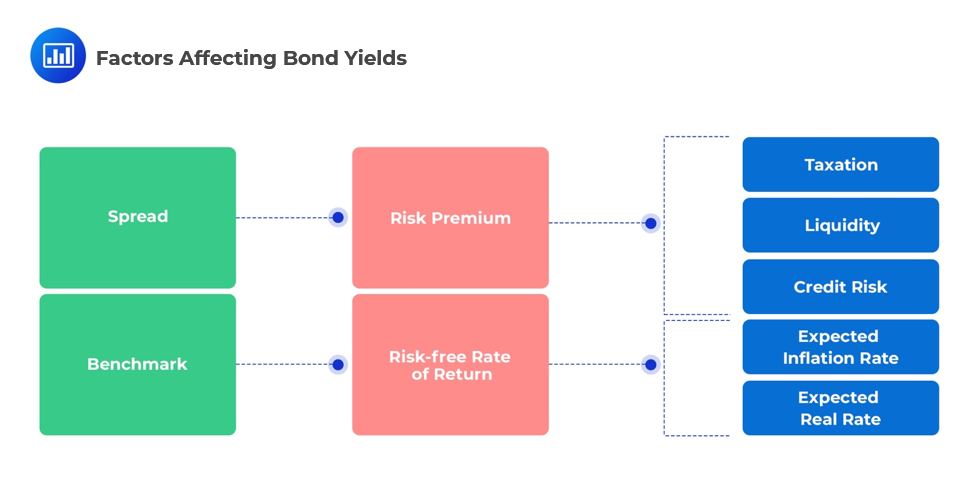 Types of Spread
Types of Spread
G-spread
G-spread (nominal spread) is the difference between the yield on Treasury Bonds and the yield on corporate bonds of the same maturity.
G-spread = Yc – Yg
Where:
Yc = yield on the non-treasury bond; and
Yg = yield on the government bond of the same maturity. I-spread
The I-spread stands for interpolated spread. It represents the difference between the yield on a bond and the swap rate (the interest rate applicable to the fixed leg in the floating-for-fixed interest rate swap, say, LIBOR). A higher I-spread means that a bond has a higher credit risk. Z-spread
The zero-volatility spread (Z-spread) is the constant spread that makes the price of a security equal to the present value of its cash flows when added to the yield at each point on the spot rate Treasury curve. It is the spread that must be added to each spot interest rate to equate the present value of the bond cash flows to the bond’s price.
Z-spread can be calculated using the following equation:
$$P=\frac { { CF }{ 1 } }{ { \left( 1+{ s }{ 1 }+Z \right) }^{ 1 } }+\frac { { CF }_{ 2 } }{ { \left( 1+{ s }_{ 2 }+Z \right) }^{ 2 } } +…+\frac { { CF }_{ n } }{ { \left( 1+{ s }_{ n }+Z \right) }^{ n } } $$
Where:
P is the price of the bond;
CF1, CF2, and CFn are the first, second and nth cash flows;
Si is the ith spot interest rate; and
Z is the zero-volatility spread. Option-Adjusted Spread (OAS)
Option-adjusted spread equals zero-volatility spread minus the value of a call option, stated in basis points. It is appropriate when measuring the yield for callable bonds.
OAS = Z-spread – Option value Question A 10% annual coupon corporate bond maturing in two years is trading at a price of 100.750. The two-year, 8% annual payment government benchmark bond is trading at a price of 100.950. The one-year and two-year government spot rates are 2.4% and 3.5%, respectively, stated as effective annual rates. The G-spread is closest to: 190 bps 200 bps 210 bpsSolution The correct answer is C. The yield-to-maturity for the corporate bond is 9.57%. $$100.75=\frac { 10 }{ \left( 1+r \right) } +\frac { 110 }{ { \left( 1+r \right) }^{ 2 } } , \quad r=0.0957$$ The yield-to-maturity for the benchmark bond is 7.47%. $$100.95=\frac { 8 }{ \left( 1+r \right) } +\frac { 108 }{ { \left( 1+r \right) }^{ 2 } } , \quad r=0.0747$$ The G-spread is 210 bps: 0.0957 – 0.0747 = 0.021
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
点击排行 |
|
推荐新闻 |
图片新闻 |
|
专题文章 |